

Short- and long-term effects of mandibular advancement device therapy for obstructive sleep apnea on temporomandibular disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis
This systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the effects of mandibular advancement device (MAD) therapy on temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) in patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).


Prediction of non-responders to oral appliance treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: a pilot study
Several clinically available variables have been identified as predictors of non-response to oral appliance (OA) treatment, including endotypical traits such as severe upper airway collapsibility, unstable ventilatory control, and low arousal threshold. This study aimed to identify potential predictors of non-response to OA treatment in patients with OSA non-adherent to treatment with positive airway pressure.


Can the use of morning occlusal guides after oral sleep appliances cause root resorption similar to orthodontic jiggling?
Objective: To evaluate root length changes associated with the use of mandibular advancement devices (MADs) to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in conjunction with morning occlusal guides.


Assessment of the causal association between obstructive sleep apnea and telomere length: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study
A plethora of observational studies has established a significant correlation between Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Telomere Length (TL). Nevertheless, a universal consensus on precise causal association and its directionality has not yet been achieved. To shed light on this, we employed Mendelian Randomization (MR) to investigate the bidirectional causal association between OSA and TL.


Adherence and Side Effects Among Patients Treated With Oral Appliance Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
The aim of this study was to evaluate the level of patient knowledge and concern for the consequences of untreated OSA, perceived partner satisfaction, and reported adverse effects, and relate these to patient adherence to OAT.

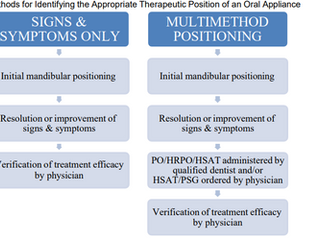
Dental Sleep Medicine Standards for Screening, Treatment, and Management of Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders in Adults Using Oral Appliance Therapy: An Update
Oral appliance therapy is a proven, effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and snoring. With more than 54 million adults having OSA in the United States, dentists play an integral role in increasing access to care for those with undiagnosed and untreated OSA.


U.S. Army Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Oral Appliance Therapy Survey: A Qualitative Analysis of Comments
The purpose of this study is to describe U.S. Army soldiers’ comments regarding obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), including effects, diagnosis, and treatment.


The Sleep Apnea-Specific Hypoxic Burden Predicts Incident Heart Failure
In comparison with apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), how does sleep apnea-specific hypoxic burden predict incident HF?


Longer respiratory events in childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome constitute a trait of older children with excessive daytime sleepiness
The objective was to evaluate the determinants of desaturation during apnea and apnea–hypopnea duration’s links with the endotypes (pharyngeal compliance, loop gain) of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and with heart rate variability (HRV) indices.


Ultrasonographic evaluation of masticatory and suprahyoid muscles in obstructive sleep apnea patients treated with mandibular advancement devices; a pilot study
This study aimed to assess the thickness and ultrasonographic pattern of the masticatory and suprahyoid muscles in OSA patients and compare the effects of mono-bloc (MB) and bibloc (BB) mandibular advancement devices (MADs) via ultrasonographic measurements.



























